

Assuming average conditions of 70 F and a barometer of 29.92 In Hg, the density of air is 0.075 Lbs/Cu Ft. The temperature in degrees Rankine is an absolute reference and is T in degrees F + 460. This is the second equation and relates ambient atmospheric pressure and temperature to density. Note that to determine the air velocity the density must first be known.

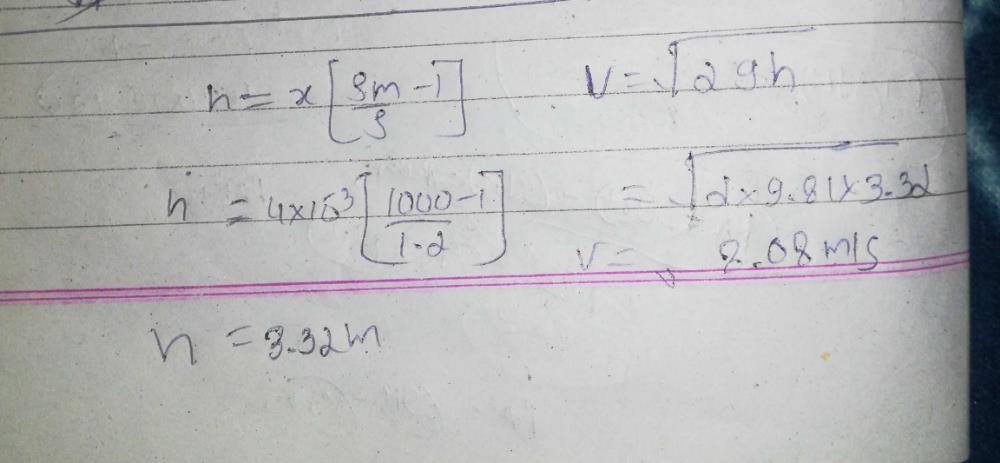
The equations that relate all these factors are: The density of the air, in turn, is a function of the local atmospheric pressure and the temperature. The pressure developed by the air velocity is called the velocity head, and it is affected by the density of the air.
#How to calculate supersonic velocity using a pitot tube full
Note that the pitot must be pointed directly into the flow – if the tube is mounted at some angle to the direction of flow, the transducer will not sense the full pressure developed by the air velocity. A differential pressure sensor like a DP15 Range Changeable Pressure Sensor can be plumbed to measure this when the pitot tube is connected on the + port and the – port is open to atmosphere. As the velocity of the air increases the pressure also increases inside the pitot tube with respect to the ambient atmosphere. The tube that is placed into the air stream is called a pitot tube after Henri Pitot, the French engineer of the early 18th century who invented it. This force can be sensed as a pressure by connecting a tube from the positive port of a differential pressure transducer like the P55 differential pressure transducer and pointing the open end of the tube directly into the oncoming air stream. This application note will describe the basic relationships between air velocity and the pressure generated by air flow.Īnyone who has put their hand out the window of a moving car has experienced the force applied by moving air. Air velocity can be measured by sensing the pressure produced by the movement of the air.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
